Imagine an operations engineer seeing through walls and floors, viewing hidden pipes, wiring, and structural components—all using just a tablet or smartphone. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality enabled by DataMesh Inspector.
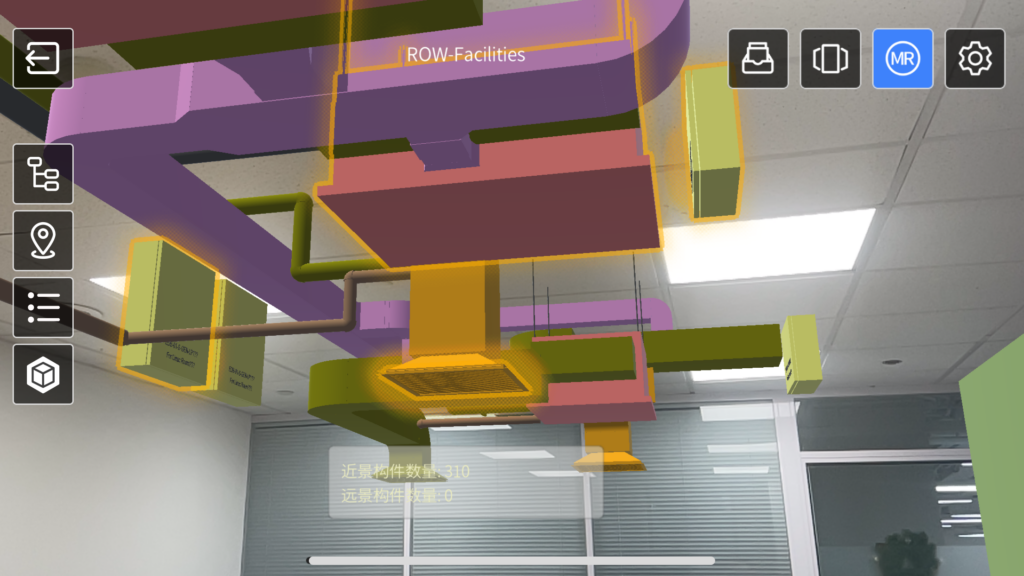
DataMesh Inspector is an innovative mixed reality and digital twin-based inspection tool designed to transform building and facility maintenance. The application allows engineers to overlay large BIM models and real-time IoT data directly onto physical sites using mobile devices, giving them “X-ray-like” vision to view building structures and facility relationships—significantly enhancing maintenance efficiency and accuracy.

DataMesh Inspector 1.2 is now available. Click here to download and experience it.
Key Features of Inspector 1.2:
- Quick Scene Creation: FactVerse’s templates and user-friendly interface enable rapid creation of digital twins and business logic for equipment newly added. Creating digital scenes has never been easier, saving significant time.
- Dynamic Loading: Cloud-based dynamic processing and loading technology supports real-time loading of massive building and facility data across mobile devices, based on user movements. No need to worry about device performance with large data volumes.
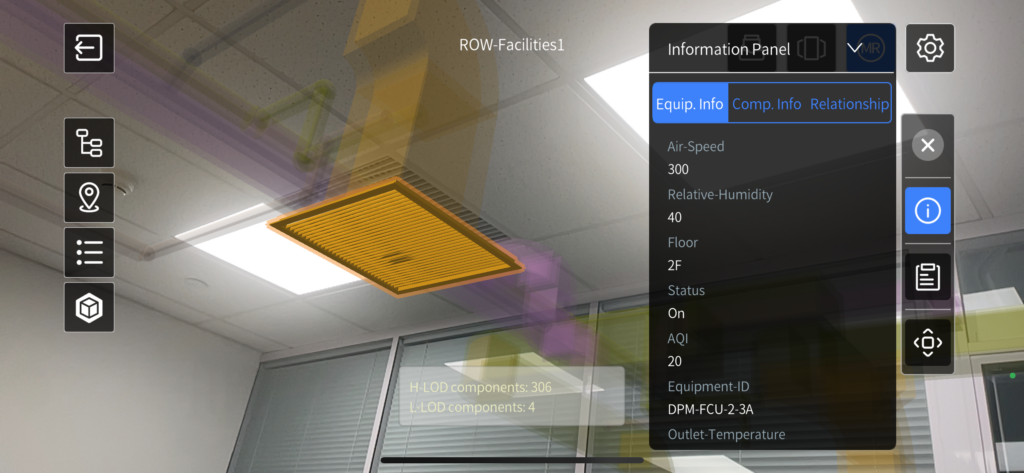
- Mixed Reality Integration: Users can overlay BIM models and IoT data, such as temperature, humidity, and energy consumption, onto the real world. This provides intuitive views of internal structures, equipment locations, and operational statuses, streamlining troubleshooting.
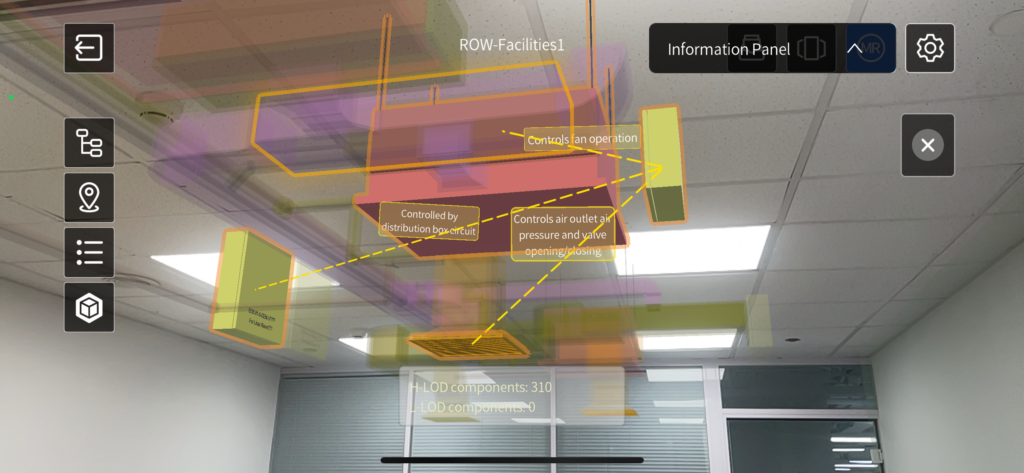
- Information & Relationships Inspection: Standardized semantic descriptions of device relationships help users easily understand system connections, hierarchical structures, pipeline routes, and the impact of faults, ensuring fast and accurate fault localization.
- Standards Compliance: FactVerse supports the Brick Schema for importing and exporting relationship structures, ensuring high compliance with green building standards in regions like Singapore.
- Multi-Device Support: Inspector is compatible with tablets and smartphones, meeting various scenario needs.
Additionally, experience and knowledge can be transformed into 3D content and projected into mixed reality scenes, allowing maintenance engineers—even those with limited expertise—to quickly grasp equipment information, such as operational statuses and maintenance procedures, enabling rapid and accurate decision-making.
How Inspector Assists in Fault Troubleshooting:
- A maintenance engineer receives an order or system alert (which can be directly pushed through Inspector).
- Upon arriving at the site, the engineer launches Inspector and scans the location code to immediately project the MR scene onto the fault area.
- In MR mode, the engineer views digital twins and real-time operational data of the equipment and facilities, performing an initial fault assessment.
- The engineer checks the business logic connections, control ranges, and impact scopes of the facilities, pinpointing key issues.
- The engineer consults maintenance documentation within Inspector to further analyze and confirm the fault, then fills out the maintenance work order.
- The engineer uploads the data, fault causes, and other information collected on-site to the system via Inspector, completing the entire process from fault reporting to MR-assisted inspection, troubleshooting, and subsequent repair.
Use Case: Air Conditioning Troubleshooting in an Office Building
Problem Discovery:
The property management team of an office building received a tenant complaint about a lack of cool air from an air conditioning vent. Maintenance engineer Mr. Wang was dispatched to investigate.
On-Site MR Inspection:
Upon arrival, Wang launched Inspector to locate potential fault points with mixed reality, checking the FCU controller and air conditioning distribution box above the ceiling. These components are typically difficult to inspect directly, but with Inspector’s MR mode, Wang could clearly identify their actual positions and statuses.
Fault Localization in MR Mode:
- Wang tapped on the digital twins of the faulty equipment to view real-time data and quickly identified an abnormal temperature at the vent.
- By further examining the device information and its relationships with other equipment, he realized that the vent was downstream of a fan coil unit (FCU) controlled by an FCU controller.
- Wang checked the current operational data of the FCU controller and the fan coil unit in the MR scene, and noticed that FCU controller appeared to be functioning correctly, but the fan coil unit showed abnormal cooling capacity, leading Wang to suspect an issue with the fan coil unit.
- Further inspection revealed a circuit breaker issue with the fan coil unit, preventing the FCU controller from controlling it, thus identifying the root cause of the fault.
Document-Aided Analysis:
To confirm the problem, Wang accessed relevant technical documents directly within Inspector and obtained the standard repair procedure for such issues.
Work Order Submission:
Finally, Wang recorded the fault details and suggested solutions in the work order and uploaded it to the system, completing the fault diagnosis in significantly less time than traditional methods, ensuring a smooth repair process.
In this case, and many others, DataMesh Inspector helps maintenance engineers efficiently locate fault causes and assess their impact, allowing them to develop targeted repair plans—reducing the time required for fault diagnosis and resolution, accelerating the repair process, and enhancing overall building and facility availability. Ultimately, this improves tenant and owner satisfaction with the building.
Inspector is evolving to further solidify its role as a crucial entry point into the FactVerse industrial metaverse platform. With its constantly expanding application scenarios, Inspector delivers long-term value for building and facility maintenance management and on-site data insights, driving the construction and building industry towards digitalization and intelligence.
Learn more about DataMesh Inspector here.
